House Building
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 1836 Accepted Submission(s): 1150 Problem Description
Have you ever played the video game Minecraft? This game has been one of the world's most popular game in recent years. The world of Minecraft is made up of lots of 1×1×1 blocks in a 3D map. Blocks are the basic units of structure in Minecraft, there are many types of blocks. A block can either be a clay, dirt, water, wood, air, ... or even a building material such as brick or concrete in this game. 
Figure 1: A typical world in Minecraft. Nyanko-san is one of the diehard fans of the game, what he loves most is to build monumental houses in the world of the game. One day, he found a flat ground in some place. Yes, a super flat ground without any roughness, it's really a lovely place to build houses on it. Nyanko-san decided to build on a n×m big flat ground, so he drew a blueprint of his house, and found some building materials to build. While everything seems goes smoothly, something wrong happened. Nyanko-san found out he had forgotten to prepare glass elements, which is a important element to decorate his house. Now Nyanko-san gives you his blueprint of house and asking for your help. Your job is quite easy, collecting a sufficient number of the glass unit for building his house. But first, you have to calculate how many units of glass should be collected. There are n rows and m columns on the ground, an intersection of a row and a column is a 1×1 square,and a square is a valid place for players to put blocks on. And to simplify this problem, Nynako-san's blueprint can be represented as an integer array ci,j(1≤i≤n,1≤j≤m). Which ci,j indicates the height of his house on the square of i-th row and j-th column. The number of glass unit that you need to collect is equal to the surface area of Nyanko-san's house(exclude the face adjacent to the ground).

Input
The first line contains an integer T indicating the total number of test cases. First line of each test case is a line with two integers n,m. The n lines that follow describe the array of Nyanko-san's blueprint, the i-th of these lines has m integers ci,1,ci,2,...,ci,m, separated by a single space. 1≤T≤50 1≤n,m≤50 0≤ci,j≤1000
Output
For each test case, please output the number of glass units you need to collect to meet Nyanko-san's requirement in one line.
Sample Input
2 3 3 1 0 0 3 1 2 1 1 0 3 3 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
Sample Output
30 20 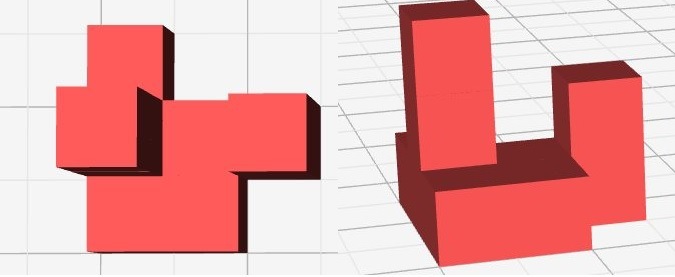
Figure 2: A top view and side view image for sample test case 1.

Source
Recommend
hujie | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you:
题意概括:此题为一道模拟题,根据题意进行模拟即可。
解题思路:
1:此题求立体的表面积,只需算出每个面的表面积即可
2:表面积包括顶面和侧面
3:让每一个立方体与其前后左右的立方体的大小进行比较,多出来的部分需要计算其表面积。
错误原因:
1: 错误地将二重循环的初始条件从零开始。因为要比较前后左右四个立方体的表面积,因此应该从1开始,才能为之后的计算留下空间。
2: 只进行了判断,忘记了进行循环。因为要比较每一个立方体与其前后左右的大小,因此应当通过循环遍历这个二维数组,才能比较出每一个立方体与其前后左右的大小。
经验总结:
1: 边界问题:对于要与边界进行比较的二维数组,可将二维数组从1(而非0)开始遍历,这样就留下了空间使此二维数组可以与周围的边界进行比较。
2: 比较前可以通过memset对整个数组初始化,方便遍历。
3: 对于只要存在就需累加的情况,可以在输入时就进行累加。只需要在输入后进行if判断即可累加。
AC代码:
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h>
int main(void) { int e[55][55]; int T, n, m, sum, i, j; scanf("%d", &T); while(T--) { sum = 0; memset(e, 0, sizeof(e)); scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); for(i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { for(j = 1; j <= m; j ++) { scanf("%d", &e[i][j]); if(e[i][j]) { sum++; } } } for(i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { for(j = 1; j <= m; j ++) { if(e[i][j] > e[i-1][j]) { sum += e[i][j] - e[i-1][j]; } if(e[i][j] > e[i+1][j]) { sum += e[i][j] - e[i+1][j]; } if(e[i][j] > e[i][j-1]) { sum += e[i][j] - e[i][j-1]; } if(e[i][j] > e[i][j+1]) { sum += e[i][j] - e[i][j+1]; } } } printf("%d\n", sum); } return 0; }